Design approach 2: The Pluriverse / Indigenous Futurism
- lfei557
- Aug 6, 2022
- 2 min read
Updated: Aug 19, 2022
The Indigenous Futurism
What is Indigenous Futurism?
What will the future be like? In 2003, Grace Dillon first coined "Indigenous Futurism" in the book Walking the Clouds: An Anthology of Indigenous Science Fiction (Vowel, 2022). It's a thought experiment that places indigenous people in a futuristic environment (Muzyka, 2019). It is an artistic movement that includes novels, video games, comic books, and other forms.

Figure 1: Dr. Grace Dillon from Portland State University
Normally, indigenous people are placed in the past without imagining what the future might look like. Indigenous futurism expresses indigenous perspectives on the future, present, and past. It considers the infinite possibilities of the future by considering how native people have lived in the past.
Many questions are now unexplained, adaptation has always been a part of Aboriginal life. For example, how aboriginal people survive severe climate disasters and how Aboriginal people responded to the effects of colonization. Reflections on these issues have led to thoughts and discussions about future issues.
What is its critique of Speculative Design?
Compared to indigenous futurism, speculative design is more unfounded and open to future predictions. Speculative design forecasts of the future are based on speculation by designers and the public and are overly concerned with aesthetics on a visual and narrative level. Proponents of indigenous futurism argue that speculative design's future fantasies are too rosy and even somewhat unrealistic to solve real-world problems.
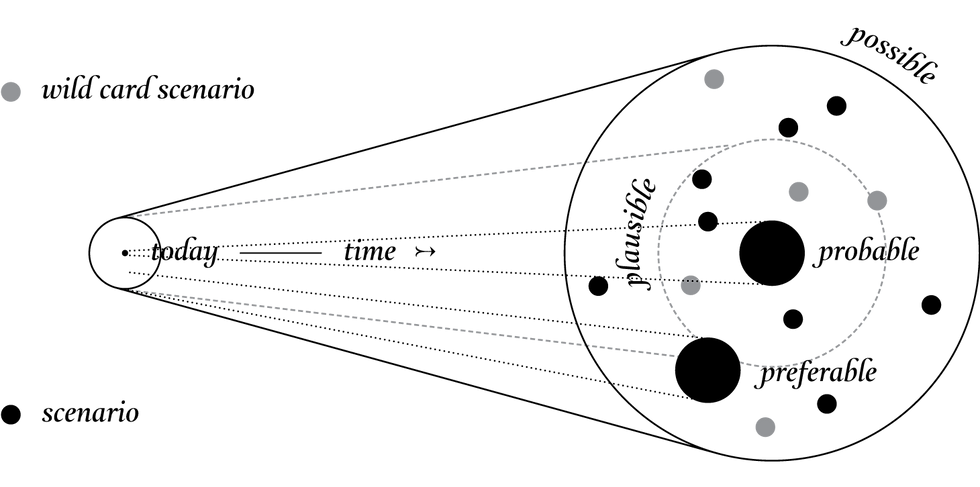
Figure 2: The Future Cone (Voros via Dunne and Raby, via Revell)
However, Indigenous futurism treats us in the present as indigenous to the future, learning from and analyzing how indigenous people in the past solved the big problems of reality and finally finding solutions to the current issues. Indigenous futurism sees a more practical way of solving problems that will occur in the future by studying past experiences than the vain predictions of speculative design.
Case study
The Things She's Seen
This is one of the widely known examples of Australian Aboriginal futurism. One example is Catching Teller Crow from The Things She's Seen. It is a Young adult fiction (YA) Indigenous Australian futurist novel. This novel is a detective thriller theme that blends realism with magic, indigenous belonging, and the concept of family obligations.

Figure 3: The Things She's Seen by Ambelin Kwaymullina and Ezekiel Kwaymullina
Although it is a YA novel, Catching Teller Crow does not shy away from the violent realities of Indigenous Australian history and racism. The book enlightens some fee Aboriginal readers with the Aboriginal perspective of two women. The author has a colonialist desire to connect Aboriginal people with non-realists.
References:
Guynes, S. (2019). Indigenous Futurism. American Book Review41(1), 6. doi:10.1353/abr.2019.0124.
Muzyka, K. (2019, March 8). From growing medicine to space rockets: What is Indigenous futurism? CBC. https://www.cbc.ca/radio/unreserved/looking-towards-the-future-indigenous-futurism-in-literature-music-film-and-fashion-1.5036479/from-growing-medicine-to-space-rockets-what-is-indigenous-futurism-1.5036480
Mitrović, I. (2015), Introduction to Speculative Design Practice, Speculative.Hr, http://speculative.hr/en/introduction-to-speculative-design-practice/
Vowel, C. (2022, June 9). Writing toward a definition of Indigenous futurism. Literary Hub. https://lithub.com/writing-toward-a-definition-of-indigenous-futurism/






Comments